
What Is Web 3.0?
The internet has evolved significantly since the inception of the first website in 1991, progressing through iterations like Web 1.0 and Web 2.0, which now captivate a staggering 63% of the world’s population. However, the eagerly anticipated and much-debated era of Web 3.0 is on the horizon, poised to redefine the digital landscape.
So, what exactly is Web 3.0?
Web 3.0 represents the latest phase in the evolution of web technologies. While still in its early stages, this new paradigm is hailed as an innovation that will revolutionize the internet, introducing concepts like decentralization, trustless or permissionless protocols, machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and more.
Despite these grand promises, the concept of Web 3.0 can be perplexing and elusive for business owners driven by IT, who are keen to implement this technology in their organizations. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into the heart of this transformative technology, examining its intersection with software development and elucidating why it holds immense significance for modern businesses.
Prepare to embark on a journey of discovery as we demystify the world of Web 3.0 and its implications. Keep reading to uncover the potential of this groundbreaking technology.
What Is the Difference Between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0?
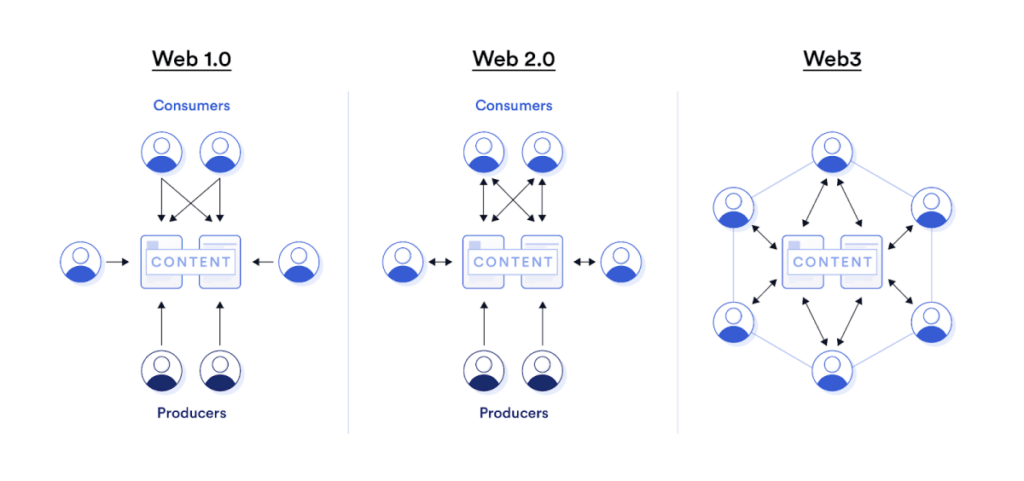
Let’s look into the history of various internet iterations to get a better perspective of what is the difference between Web2.0 and Web 3.0. In Web 1.0, the internet was generally “static” where users could do nothing more beyond browsing read-only web pages. At the same time, content creators were a select few who had the resources to build websites and the whole IT infrastructure.
The Web 2.0 era was marked by the 2004 O’Reilly Media and MediaLive conference, which highlighted innovative software applications that could be built on the Web. YouTube became the first website to experiment with the Web 2.0 internet revolution, by creating a dynamic space where users could now interact amongst themselves, create content, and even share the same with others. Look at it as a read-and-write internet iteration.
Fast forward to Web 3.0, users can now read, write, and truly own the content that they create on the internet. That said, here are the main differences between Web 2.0 and Web 3.0.
The Power Of Data Ownership
Data ownership is a grey area that often raises many consumer concerns. Both Web 1.0 and Web 2.0 internet iterations gave the power of user data ownership to service providers and dominating tech giants. Although users usually consent to this permission, Web 2.0 tech giants often end up misusing the data by monetizing it for their own gains.
In Web 3.0, the idea is that of a decentralized internet where every user owns their online activity data and will choose who they want to give access to or how they want to monetize the same. Typically, user data in Web3 is stored on a decentralized blockchain, as opposed to centralised servers, owned and managed by tech giants, such as Google, Amazon, or Facebook.
New Emerging Technologies
The emergence and spread of Web 2.0 were greatly influenced by the rise of cloud computing, social media, and smartphone mobile technologies. On the other hand, the Web3 feature, concept, and ideals largely hinge on the prevalence of blockchain, artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), decentralisation, and edge computing technologies.
The Core Features of Web 3.0

Web 3.0 technology is still nascent and has a long way to go. Nonetheless, three core features help define how this new internet iteration will look when it finally goes mainstream. They include:
Decentralisation
The core tenet of the latest World Wide Web (WWW) iteration of the internet is decentralisation. Unlike in Web 2.0 where computers leverage HTTP to create unique web addresses that are stored in centralised servers and databases, Web 3.0 internet content is stored in decentralized web nodes. This means that users can own any disparate data generated from smartphones, sensors, or even appliances and monetize the same on decentralized data networks. Database giants such as Meta and Google will most likely become irrelevant when Web 3.0 matures.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) Computing
The fundamentals of Web3.0 and the IoT include an internet where computers can understand information from a human perspective. This will be driven by a host of emerging technologies, such as artificial intelligence, semantic web concepts, machine learning, and natural language processing. With this approach, robots and computers will help drive faster and more accurate results in research and development fields, such as drug manufacturing.
End-to-End Ubiquity and Connectivity
Web 3.0 and the IoT will coexist hand in hand to drive an internet where data or content is ubiquitous and seamlessly connected. Connected devices, including smartphones, laptops, and Bluetooth gadgets will be connected, allowing users to communicate and share content around the world with an end-to-end loop experience. Moreover, this will give rise to IoT devices that self-report in real-time as opposed to devices that require human intervention to do the same. With this approach, businesses will have access to important information as the data surface, enabling simultaneous sorting and analyses.
Trustless and Permissionless
The Web 3.0 internet doesn’t only hinge on open-source software applications but is also inherently trustless. In other words, users can join any blockchain network and interact amongst themselves without the intervention of a central authority or trusted intermediary. At the same time, Web 3.0 is permissionless, which allows anyone to join and participate, or even form the governing body of powerful decentralized autonomous organisations (DAOs). This feature will also promote shared economies, which will likely redefine how businesses operate in the near future.
Web 3.0 and Software Development
The whole idea around Web 3.0 and software development is to streamline the overall building process and optimise easier or faster internet searches by users. Delving deeper into how Web 2.0 and Web 3.0 applications work will help put this into better perspective. In Web 2.0. users only interact with the front-end side of any application built on its iteration. Technically, the front end communicates with the back end, which then connects to the application’s database. While all this is happening, the application’s code is hosted in centralised servers. Users usually don’t have access to these servers via their end browsers.
Web3 applications eliminate the need for centralised databases and backend logic servers altogether. Instead, applications are built and deployed on-chain, in a decentralized state machine, which is maintained and supported by anonymous web nodes. The application’s logic resides in on-chain smart contracts, which are programmed by developers and deployed on the decentralized state machine.
Here is a visual representation of how Web 3.0 applications work:
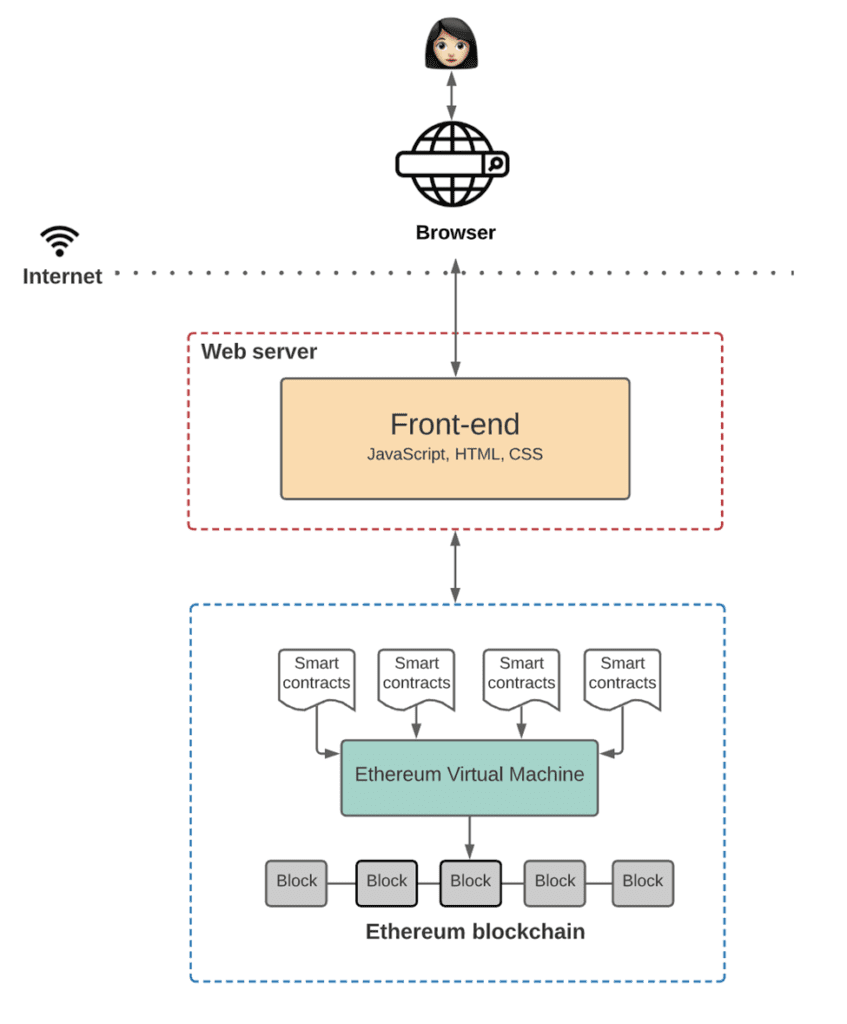
Software Development Architecture in Web 3.0
Now that you understand what is web 3.0, here is what constitute the primary architecture elements
The Underlying Blockchain
Although there are many blockchain solutions for building decentralized applications, the Ethereum network is the most popular one among businesses and developers. Besides being globally accessible, the Ethereum blockchain features a deterministic state machine that is supported by an independent peer-to-peer nodes network.
Any developer in the world can access the “state machine” blockchain where they can write but not update captured data. Moreover, the Ethereum blockchain is publicly owned by every computing node on the network, making it a truly decentralized We 3.0 solution.
Smart Contracts
On top of building blockchain applications, developers usually write smart contracts using advanced programming languages, such as Solidity or Vyper. The smart contracts reside and run on the blockchain. They automatically execute and define the logic behind an application’s state changes on the blockchain. Technically, smart contracts are transparent and public, meaning any user can inspect them to explore the logic of the application in question.
Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)
The Web 3.0 architecture also features the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), a system that executes the logic defined in smart contracts. The EVM processes all the state changes that happen within a specifically defined logic on the state machine. It’s also worth mentioning that developers usually tweak advanced programming languages, such as Vyper and solidity into bytecode, which can easily be executed by the EVM.
Frontend
Decentralized applications function like any other Web 2.0 digital solution when it comes to user experience (UI). That said, a typical software development process in Web 3.0 will include a front-end design that defines the underlying UI logic, as well as connects the same with smart contracts
The Benefits of Web 3.0
Early Web 3.0 adopters and enthusiasts believe that this technology marks the beginning of a more secure, transparent, and intelligent internet experience for all levels of users. Most importantly the tech will likely redefine machine-human interactions in the virtual world. With that in mind, here are the benefits of Web 3.0 and why they matter from business and user perspectives.
An Internet with No Restrictions
The Web 3.0 ideals border with decentralisation and democratisation of the internet, to make online products and services accessible to all levels of users, regardless of their geographical location, social background, income, or even gender. Any user can create and truly own a unique address within blockchain networks to transfer digital assets or socialise across the globe in real-time.
Enhanced Transparency
Blockchain infrastructures, which are the backbone of Web 3.0 are inherently transparent. All blockchain networks, whether Ethereum, Solana, Binance Smart Chain (BSC) or even Flow, allow users to track their online activity and inspect an application’s code. On top of that, most blockchains are built by non-profit Web 3.0 communities, making them open-source solutions, inviting developers to try open designs and processes.
Greater Privacy and Data Control
Greater data privacy and control is likely the greatest and most defining advantage of all the benefits of Web 3.0. Web 3.0 encrypts user data, locking out giant tech players, such as Google or Amazon from controlling a customer’s personal information. Even better, complete data ownership and control means users can decide who to share their information with or even sell the same to advertising brands and directly benefit from the monetization.
Seamless End-to-End Services
With decentralized data storage and access as the primary selling point, Web 3.0 allows users to sync their data across the internet and access the same under any circumstance. Multiple backups ensure an end-to-end user experience, which is usually interrupted in Web 2.0 when servers fail. At the same time, tech giants or institutions won’t suspend user accounts anyhow.
Better Data Processing Capabilities
Web 3.0 is most likely going to complement big data technology in better and more innovative ways. The internet iteration works seamlessly with emerging big data technologies, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence to help businesses draw valuable insights from huge data sets. This will be in conducting in-depth client-demand analyses or even offering personalised customer experiences.
Open, Accessible, and Connected Data
The idea behind Web 3.0 and the IoT is to enhance data gathering and utility. Technically, any user on the internet can connect their smartphone or device to a network of other devices and access the data from their end if synced. At the same time, everyday users can access and interact with most decentralized applications without traditional Web 2.0 bottlenecks, such as paying third-party access fees.
Single Profile User Experience
Unlike the internet experience in Web 2.0. where users need multiple profiles to access different social media platforms, Web 3.0 promotes a single profile experience. This means a user can create one avatar and use it to access any decentralized social network, or even attend “in-person” virtual events in the Metaverse.
Key Take Away
As digitization continues to penetrate every corner of the globe, internet users are increasingly becoming concerned about how tech giants access and monetize their data. Web 3.0 internet iteration is stepping in at the right time to hand over the power of data privacy and control to users. And with the rapid innovation in the industry, businesses are accelerating this future of decentralized, transparent online activity by adopting blockchain solutions. It will be fascinating to see how Web3.0 Software development providers evolve with this trend.